Cells that make up animal tissues are sometimes woven together with extracellular fibers and are occasionally held together by a sticky substance that coats the cells. Cellulose which is a polymer of glucose with exclusive β-14 linkages between the units Figure 2174 is an important structural component of plants and fungi cells.

What Are Lipids Structure Function Expii
When many phospholipids line up they form a double layer that is.

. Z explain the term karyotype and mention the karyotype analysis. Ether chloroform acetone benzene and general insolubility in water. The term chromatin is used to describe chromosomes the protein-DNA complexes when they are both condensed and decondensed.
They are made of a hydrocarbon chain that terminates with a carboxylic acid group. When the cell is in the growth and maintenance phases of its life cycle numerous proteins are still associated with the nucleic acids but the DNA strands more closely resemble an unwound jumbled bunch of threads. Like other macromolecules nucleic acids are composed of monomers called nucleotides which are polymerized to form large strandsEach nucleic acid strand contains certain nucleotides.
For the most part the two are used to describe the cytoplasm of protozoa amoeba in particular that varies in structure location and function. Round flat long and thin short and thick and size eg. Lipids perform functions both within the body and in food.
With regards to location the cytoplasm is also divided into the two layers. These include the ectoplasm and the endoplasm. All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum ER.
This arrangement confers the molecule with a polar. Within the body lipids function as an energy reserve regulate hormones transmit nerve impulses cushion vital organs and transport fat-soluble nutrients. Fatty acids or fatty acid residues when they are part of a lipid are a diverse group of molecules synthesized by chain-elongation of an acetyl-CoA primer with malonyl-CoA or methylmalonyl-CoA groups in a process called fatty acid synthesis.
Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. Endoplasmic reticulum ER in biology a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions being important particularly in the synthesis folding modification and transport of proteins. In Microbial Metabolism we discussed three classes of macromolecules.
The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility in nonpolar organic solvents eg. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body which vary in shape eg. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membraneLipids are molecules that include fats waxes and some vitamins among others.
Proteins lipids and carbohydratesIn this chapter we will discuss a fourth class of macromolecules. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids a phosphate group and a glycerol molecule. Z justify the need for cell division.
Z describe various phases of cell cycle. Fat in food serves as an energy source with high caloric density adds texture and taste and contributes to satiety. This two minute tutorial describes how the sodium-potassium pump uses active transport to move sodium ions Na out of a cell and potassium ions K into.
There is great structural variety among the lipids as will be demonstrated in the following sections. Different types of tissues can also be arranged together to form organs. A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism and all living structures in the human body are made of cells.
Small granule cells of the cerebellum in the brain 4 micrometers up to the huge oocytes eggs. Z describe the general importance of the cell molecules-water mineral ions carbohydrates lipids amino acids proteins nucleotides nucleic acids enzymes vitamins hormones steroids and alkaloids. The picture you have in your mind of the nervous system probably includes the brain the nervous tissue contained within the cranium and the spinal cord the extension of nervous tissue within the vertebral columnThat suggests it is made of two organsand you may not even think of the spinal cord as an organbut the nervous system is a very complex structure.
In animal cells the ER usually. Phospholipid Bilayer Structure. An additional function of polysaccharides in cells relates to structure.
Tissues are groups of cells with both a shared structure and function. The phospholipid bilayer is made of two layers of phospholipids.

Fatty Acid Definition Structure Functions Properties Examples Britannica

Structure And Function Of Lipids Youtube

Lipids Definition Structure And Functions Fatty Acids
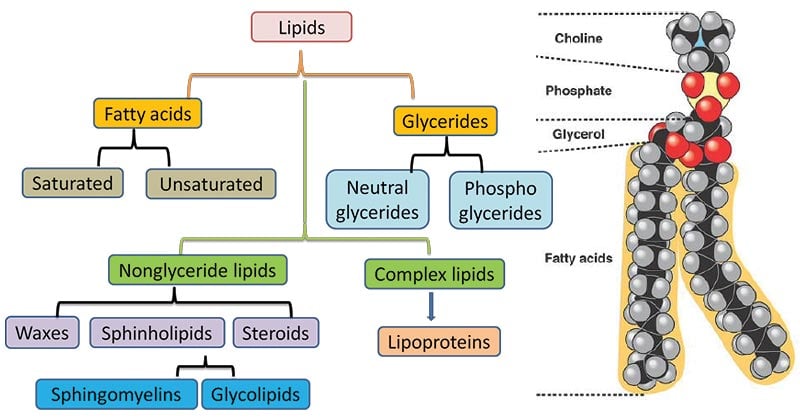
Lipids Definition Properties Structure Types Examples Functions
0 Comments