Principal quantum number describes. C The magnetic quantum number m l describes the orientation of the orbital.

What Are The Possible Orbitals For N 3 In 2022 Electron Configuration Energy Level Quantum
L0 for an s orbital l-1 for a p orbital l2 for a d orbital and so on.

. D An orbital is the path that an electron follows during its movement in an atom. The_____quantum number defines the shape of an orbital Quantum Numbers and Shapes of Orbitals - The Fact Factor Quantum number - Wikipedia Quantum number - Wikipedia The azimuthal quantum number is a quantum number for an atomic orbital that determines its orbital angular momentum and describes the shape of the orbital. The angular momentum quantum number describes the the size and energy associated with an orbital.
10th - 11th grade. They can even take on more complex shapes as the value of the angular quantum number becomes larger. Angular Momentum Quantum Number l The angular momentum quantum number signified as l describes the general shape or region an electron occupiesits orbital shape.
Angular momentum quantum number l describes the shape of the orbitals. Spin of electron d. A 1 B 2 C 0 D 3 E 4 26.
An orbital is the path that an electron follows during. The value of ________ called the __________________ quantum number designates the spatial orientation of an orbital. The magnetic quantum number m describes the orientation of the orbital.
Angular momentum quantum number. Schrödinger quantum number spin quantum number principal quantum number magnetic quantum number If two electrons in the same atom have the same value of l they are in the same sublevel but not necessarily in the same level. Size of the orbital.
Hence option B is the correct one. It describes the quantum state of an electron including its energy orbital shape and orbital orientation. The second quantum number known as the angular or orbital quantum number describes the subshell and gives the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum through the relation.
Spin of an electron. Shape of orbital b. The principal quantum number of an orbital is n 1.
What are possible values for quantum numbers. Two aqueous solutions are both at room temperature and are. This must be a n ____ orbital.
29 rows For s orbital Azimuthal quantum number 0 and the magnetic. Principle quantum number describes. Size of the orbital c.
What value of l is represented by an g orbital. In chemistry and spectroscopy ℓ 0 is called an s orbital ℓ. L determines the shape of an atomic orbital.
Azimuthal quantum number describes the shape of the orbital and represented by l and spin quantum number describes the spin of the electron and magnetic. Each element has an electron configuration that can be expressed in quantum numbers Each orbital in an atom consists of 4 quantum numbers each describing the state of the orbital n the principal quantum number. The principal quantum number n describes the shape of an orbital b.
C the magnetic quantum number ml describes the orientation of the orbital. The size of the orbitals. The value of l depends on the value of the principle quantum number n.
The angular quantum number l describes the shape of the orbital. B The angular momentum quantum number l describes the the size and energy associated with an orbital. Which of the following quantum numbers describes the shape of an orbital.
Which of the following quantum numbers describes the shape of an orbital. Orientation of in the orbital electron cloud. Orientation of in the orbitalelectron cloud.
Orientation in the orbital electron cloud. Principal Quantum number describes- a. The four quantum numbers are called the principal or shell quantum number n the momentum or subshell quantum number l the magnetic quantum number m and the spin quantum number s.
Size of the orbital. B the angular momentum quantum number l describes the size and energy associated with an orbital. The principal quantum number therefore indirectly describes the energy of an orbital.
The correct option is ii. Size of the orbital. If the principal quantum number has the value of 5 it refers to the orbital 5s5p5d and 5f orbitals.
The angular momentum quantum number l also referred to as the secondary quantum number or azimuthal quantum number describes the shape of the orbital that an electron occupies. In the same orbital. Each wavefunction with a given set of values of n l and m l describes a particular spatial distribution of.
Orbitals have shapes that are best described as spherical l 0 polar l 1 or cloverleaf l 2. Correct option is B Principal quantum number n. Thus the principal quantum number describes the size of the orbital.
The angular momentum quantum number can have positive values of zero to n 1. A The principal quantum number n describes the shape of an orbital. The angular momentum quantum number is a quantum number that describes the shape of an orbital and tells us which subshells are present in the principal shell.
A magnetic quantum number B principal quantum number C angular momentum quantum number D spin quantum number E Schrödinger quantum number 25. A magnetic quantum number B principal quantum number C angular momentum quantum number D spin quantum number E Schrödinger quantum number 25. The magnetic quantum number m l can have 2l 1 integral values ranging from l to l and describes the orientation of the electron distribution.
Answer 1 of 2. A the principle quantum number n describes the shape of an orbital. Asked Aug 18 2020 in Chemistry by alyssaindelicato.

Principle Quantum Number N 1 2 3 Describes Orbital Size And Energy Angular Momentum Quantum Number L 0 To N 1 Describes Orbital Shape Magnetic Ppt Download

Quantum Numbers Video Quantum Physics Khan Academy
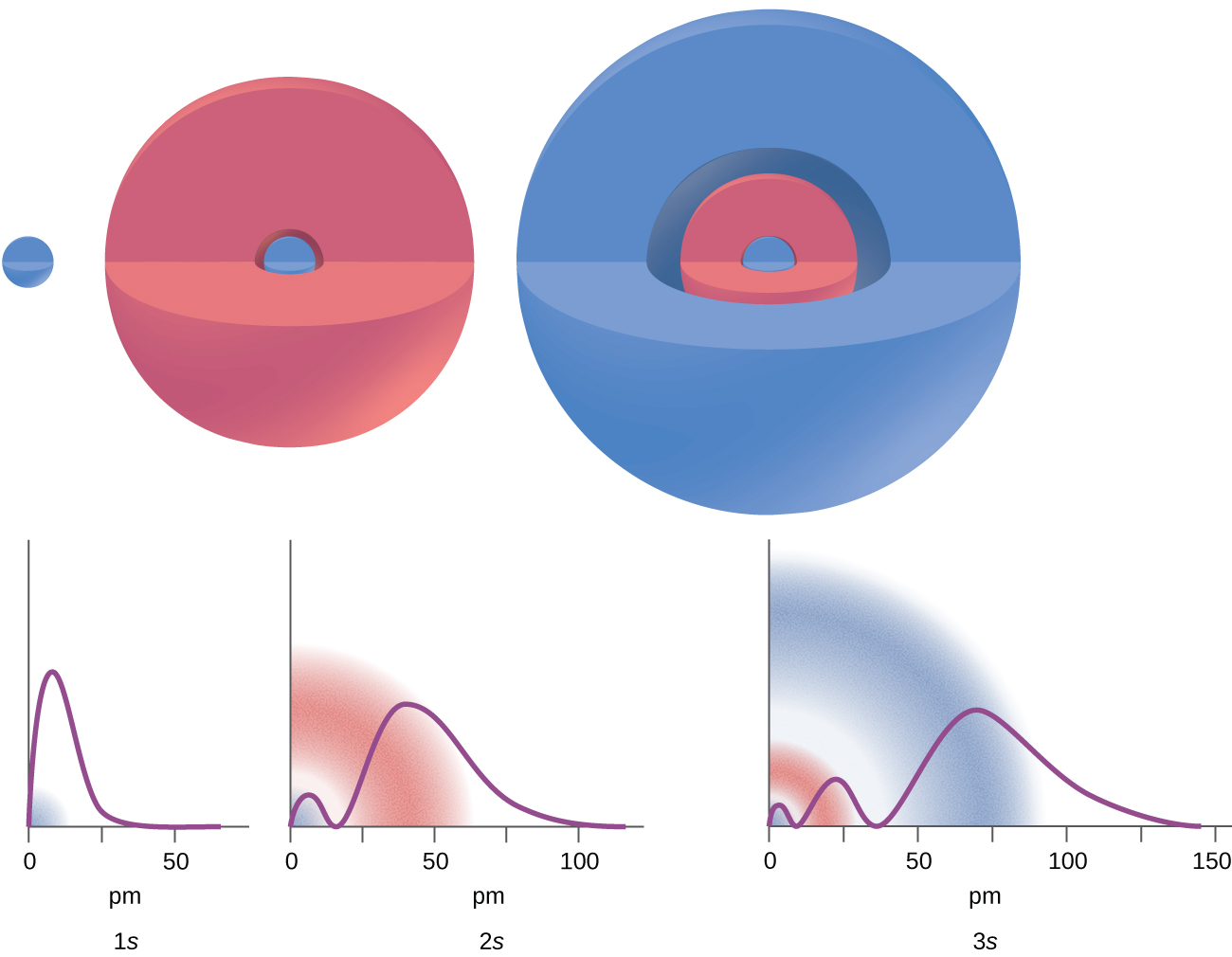
2 2 Atomic Orbitals And Quantum Numbers Chemistry Libretexts
0 Comments